The stock market can be a complex environment, especially for new investors. One of the key aspects of trading is understanding the various types of orders you can place. Each type of order serves a different purpose and can have a significant impact on your trading strategy. This guide will explore the different types of orders available in the stock market, their functionalities, and how they can be used effectively to meet your investment goals.

1. Market Orders
What is a Market Order?
A market order is the most straightforward type of order. It instructs your broker to buy or sell a stock immediately at the best available price. Market orders are executed as quickly as possible, which means the price at which the order is executed might differ from the price quoted when you placed the order.
Advantages of Market Orders
- Speed: Market orders are executed almost instantly, making them ideal for traders who want to enter or exit a position quickly.
- Simplicity: This type of order is easy to place and does not require specifying a price.
Disadvantages of Market Orders
- Price Uncertainty: The actual execution price may be different from the price you saw when placing the order, especially in fast-moving or volatile markets.
- Slippage: In highly volatile markets, the price at which your order is executed might be significantly different from the last traded price.
When to Use Market Orders
Market orders are best used when you want to buy or sell a stock quickly and are less concerned about the exact price. They are commonly used for highly liquid stocks where the difference between the bid and ask prices is minimal.
2. Limit Orders
What is a Limit Order?
A limit order is an order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better. For a buy limit order, the order will only be executed at the specified price or lower. For a sell limit order, it will be executed at the specified price or higher.
Advantages of Limit Orders
- Price Control: You can specify the price at which you are willing to buy or sell, which helps in managing the cost of transactions.
- Protection Against Slippage: Limit orders prevent you from paying more than you intend or selling for less than you want.
Disadvantages of Limit Orders
- Execution Uncertainty: There is no guarantee that your order will be executed, especially if the stock does not reach your specified price.
- Order Duration: If the stock does not reach the limit price, the order may remain unfilled for an extended period or until it expires.
When to Use Limit Orders
Limit orders are ideal when you have a specific price in mind and are not in a hurry to execute the trade. They are useful in markets with lower liquidity or for stocks with wider bid-ask spreads.
3. Stop Orders
What is a Stop Order?
A stop order, also known as a stop-loss order, is used to limit potential losses or protect gains on a position. A stop order becomes a market order once the stock reaches a predetermined price level, known as the stop price.
Types of Stop Orders
- Stop-Loss Order: This is placed to sell a stock if its price falls to a certain level. It helps limit losses if the market moves against your position.
- Stop-Limit Order: This combines the features of a stop order and a limit order. Once the stop price is reached, the order becomes a limit order, meaning it will only be executed at the limit price or better.
Advantages of Stop Orders
- Automatic Execution: Stop orders automatically trigger once the stop price is reached, which helps in managing trades without constant monitoring.
- Loss Limitation: They help in limiting losses and protecting gains by setting predefined exit points.
Disadvantages of Stop Orders
- Price Impact: In fast-moving markets, stop orders may lead to execution at unfavorable prices.
- No Guarantee of Execution: Stop orders can sometimes be executed at a price significantly worse than the stop price, especially in volatile markets.
When to Use Stop Orders
Stop orders are useful for managing risk and protecting investments. They are ideal for investors who want to limit potential losses or lock in gains but cannot continuously monitor the market.
4. Trailing Stop Orders
What is a Trailing Stop Order?
A trailing stop order is a dynamic type of stop order that adjusts automatically as the stock price moves in your favor. It helps lock in profits while allowing the position to benefit from favorable price movements.
How Does a Trailing Stop Order Work?
- Trailing Stop-Loss Order: This order moves up with the stock price. If the stock price increases, the stop price adjusts upwards, maintaining a specified distance from the current market price. If the stock price falls, the stop price remains unchanged and triggers a sell order if reached.
- Trailing Stop-Limit Order: Similar to a trailing stop-loss order, but once the stop price is reached, it becomes a limit order instead of a market order.
Advantages of Trailing Stop Orders
- Profit Protection: Trailing stops help in locking in profits as the stock price rises while providing downside protection.
- Automatic Adjustment: They adjust automatically, removing the need for manual updates.
Disadvantages of Trailing Stop Orders
- Execution Risk: In volatile markets, the final execution price might be worse than the stop price, especially with trailing stop-limit orders.
- Potential for Premature Exit: In highly volatile markets, the stock price might temporarily dip below the trailing stop price, leading to an early exit.
When to Use Trailing Stop Orders
Trailing stop orders are ideal for investors who want to secure gains and manage risk dynamically as the market moves. They are suitable for trending stocks where you want to capture as much profit as possible while protecting against adverse price movements.
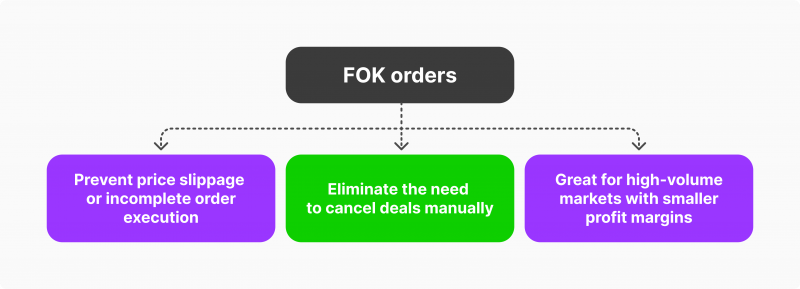
5. Fill or Kill (FOK) Orders
What is a Fill or Kill (FOK) Order?
A Fill or Kill (FOK) order is a type of order that must be executed in its entirety immediately or not at all. If the entire order cannot be filled at once, it is canceled.
Advantages of FOK Orders
- Immediate Execution: FOK orders ensure that you receive the full quantity of shares at once or not at all, avoiding partial fills.
- Clarity: They provide clear terms for order execution, which can be useful for large trades.
Disadvantages of FOK Orders
- Execution Risk: FOK orders may not be filled if there is insufficient liquidity at the desired price.
- Market Impact: Large FOK orders can impact the market price, especially if they involve significant quantities of shares.
When to Use FOK Orders
FOK orders are useful when you need to execute a large trade immediately and require the entire order to be filled at once. They are often used by institutional traders and in situations where liquidity is sufficient to support the trade.
6. Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Orders
What is an Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Order?
An Immediate or Cancel (IOC) order is similar to a FOK order but allows for partial execution. Any portion of the order that cannot be filled immediately is canceled.
Advantages of IOC Orders
- Partial Execution: IOC orders can be partially filled, providing flexibility if the full order cannot be executed right away.
- Quick Execution: They ensure immediate execution of the portion that is available, which can be advantageous in fast-moving markets.
Disadvantages of IOC Orders
- Partial Fills: Only part of the order may be executed, and the remaining portion will be canceled, which might not always align with your trading strategy.
- Execution Uncertainty: There is no guarantee that even the partial fill will be completed at the desired price.
When to Use IOC Orders
IOC orders are suitable when you want immediate execution of a part of your order while accepting that the rest might not be filled. They are useful in high liquidity situations where partial fills are acceptable.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of orders in the stock market is crucial for effectively managing your trades and investments. Whether you are aiming for quick execution with market orders, precise price control with limit orders, or risk management with stop orders, each type of order has its own advantages and disadvantages. By selecting the appropriate order type based on your trading goals and market conditions, you can enhance your trading strategy and better navigate the complexities of the stock market.
Keep in mind that the choice of order type should align with your overall trading strategy, market conditions, and investment objectives. As markets evolve and new trading technologies emerge, staying informed about order types and their functionalities will help you make more informed and effective trading decisions.
You might also be interested in – Understanding the Difference Between Record Date and Ex-Dividend Date